 Fred's ImageMagick Scripts
Fred's ImageMagick Scripts
Copyright © Fred Weinhaus My scripts are available free of charge for non-commercial (non-profit) use, ONLY. For use of my scripts in commercial (for-profit) environments or non-free applications, please contact me (Fred Weinhaus) for licensing arrangements. My email address is fmw at alink dot net. If you: 1) redistribute, 2) incorporate any of these scripts into other free applications or 3) reprogram them in another scripting language, then you must contact me for permission, especially if the result might be used in a commercial or for-profit environment. Usage, whether stated or not in the script, is restricted to the above licensing arrangements. It is also subject, in a subordinate manner, to the ImageMagick license, which can be found at: http://www.imagemagick.org/script/license.php Please read the Pointers For Use on my home page to properly install and customize my scripts. |
|
Finds the four corners of a binary quadrilateral by finding maximum curvature on the convex hull outline. |
last modified: January 07, 2025
|
USAGE: quadcorners2 [-L lower] [-U upper] [-a area] [-o openM] [-c closeM]
[-b blursize] [-f filtersize] [-s skip] [-i images] [-k kind] [-C color] [-r radius]
[-t textoffset] infile
-p ... pad .......... border pad amount for input image to help in getting PURPOSE: To optionally threshold an image if not already binary and find the four corners of the binary quadrilateral from the maximum curvature of the outline obtained from the convex hull.
DESCRIPTION: QUADCORNERS2 optionally thresholds an image, if not already binary,
and finds the four corners of a quadrilateral in the binary image. The process is
1) optionally color threshold the image; 2) optionally apply morphology to clean
and smooth the outline of the image; 3) optionally apply connected components
processing to remove small regions; 4) get a white filled convex hull on black
background image 5) convert the convex hull image to polar coordinates
and scale to 1 row; 6) extract the reverse polar coefficients; 7) convert the
1D polar image heights to 1D x and y images using the reverse coefficents;
8) apply 1D first and second order derivative to the 1D x and y images;
9) use the x and y derivatives to compute a 1D curvature image; 10) find the
x locations in the 1D curvature image where the curvature is maximum skipping
enough between peaks; 11) look up the x and y coordinates associated with peaks
locations; 12) sort the top 4 peak x,y coordinates in TL, TR, BR, BL order
(i.e., clockwise from TL)
ARGUMENTS: -p pad ... PAD is the border pad amount for input image to help in getting good Hough lines; integer>=0; default=0 (no padding) -L lower ... LOWER color threshold for extracting quadrilateral; comma separated triplet in the form of either 8-bit grayscale or percent color values (for srgb color); if only 1 value provided, it will be duplicated three times; default=50% (mid-gray) -U upper ... UPPER color threshold for extracting quadrilateral; comma separated triplet in the form of either 8-bit grayscale or percent color values (for srgb color); if only 1 value provided, it will be duplicated three times; default=100% (white) -a area ... AREA threshold in pixels for removing small regions from the thresholded image; integer>=0; default=0 (skip connected components filtering) -o openM ... OPENM is the morphology open diamond size for preprocessing to remove all white regions outside the main quadrilateral in the threshold image; integer>0; default is no morphology open -c closeM ... CLOSEM is the morphology close disk size for preprocessing to remove all black regions inside the main white quadrilateral in the threshold image; integer>0; default is no morphology close -b blursize ... BLURSIZE is the (half) size of the 1D blur smoothing filter (in pixels); integer>0; default=5 -f filtersize ... FILTERSIZE is the (half) size of the 1D derivative filters (in pixels); integer>0; default=5 -s skip ... SKIP (in pixels) is the minimum distance between peaks in the polar image; integer>0; default=50 (must be larger than the filtersize) -i images ... IMAGES specifies whether to keep ancillary processing images (especially for debugging); choices are: view (v) or save (s); default is neither -k kind ... KIND of ancillary processing images; choices are: threshold (t), cleaned (c), (convex) hull (h), polar (p), final (corners) (f), or all (a) -C color ... COLOR used when drawing on various images; any IM color value is allowed; default=red -r radius ... RADIUS for circle used to mark corner points; integer>0; default=2 -t textoffset ... text offset of TL, TR, BR, BL annotation relative to corner points; +X+Y format, integers for X and Y; default="+0-15" REQUIREMENTS: Requires IM 7 due to the use of -color-threshold and the convex hull CAVEAT: No guarantee that this script will work on all platforms, nor that trapping of inconsistent parameters is complete and foolproof. Use At Your Own Risk. |
|
Example 1: Binary Rectangle Input |
|
Original Image |
|
|
arguments: |
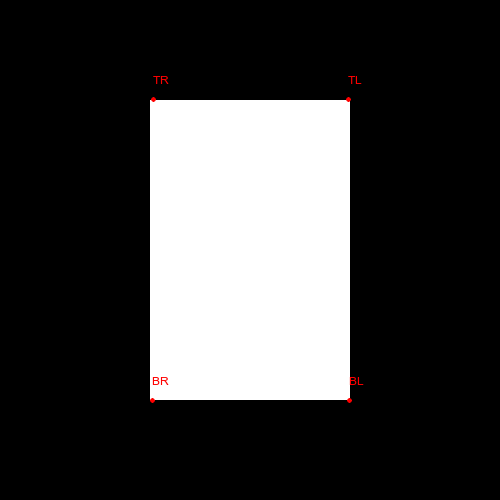
|
|
Example 2: Binary Quadrilateral Input |
|
Original Image |

|
|
arguments: |

|
|
Example 3: Quadrilateral in Non-Binary Image |
|
Original Image |

|
|
arguments: |
|
Thresholded Image |

|
|
Cleaned Image |
|
|
Convex Hull Image: |

|
|
Polar Image |

|
|
Final Corners Image |

|
|
What the script does is as follows:
|